Hydropower Industry Launches Major International Project to Demonstrate Flexibility
Credit to Author: Sonal Patel| Date: Wed, 11 Dec 2019 14:15:32 +0000
The post Hydropower Industry Launches Major International Project to Demonstrate Flexibility appeared first on POWER Magazine.
In a new attempt to secure a concrete role for the international hydropower industry within the decarbonization movement, several utilities, equipment manufacturers, universities, research centers, and consultancies have scaffolded to demonstrate how modern hydropower plants can provide flexibility to markets that are increasingly inundated by variable generation like wind and solar.
On Dec. 10, the European Commission and a consortium of 19 partners launched the four-year XFLEX HYDRO (Hydropower Extending Power System Flexibility) project at the ongoing United Nations (UN) climate change conference (COP25) in Madrid, Spain. The €18 million ($20 million) initiative’s main goal is to increase hydropower’s potential in terms of plant efficiency, “thereby boosting electrical power systems and enabling plant and system operators to operate more successfully in electricity markets,” said Patrick Child, Deputy Director-General for the European Commission’s Directorate-General Research and Innovation.
Concerted Focus on Variable Speed Systems
Over the next four years, flexibility technologies will be tested in the project’s three phases—innovation, demonstration, and deployment—at seven existing European hydropower stations.
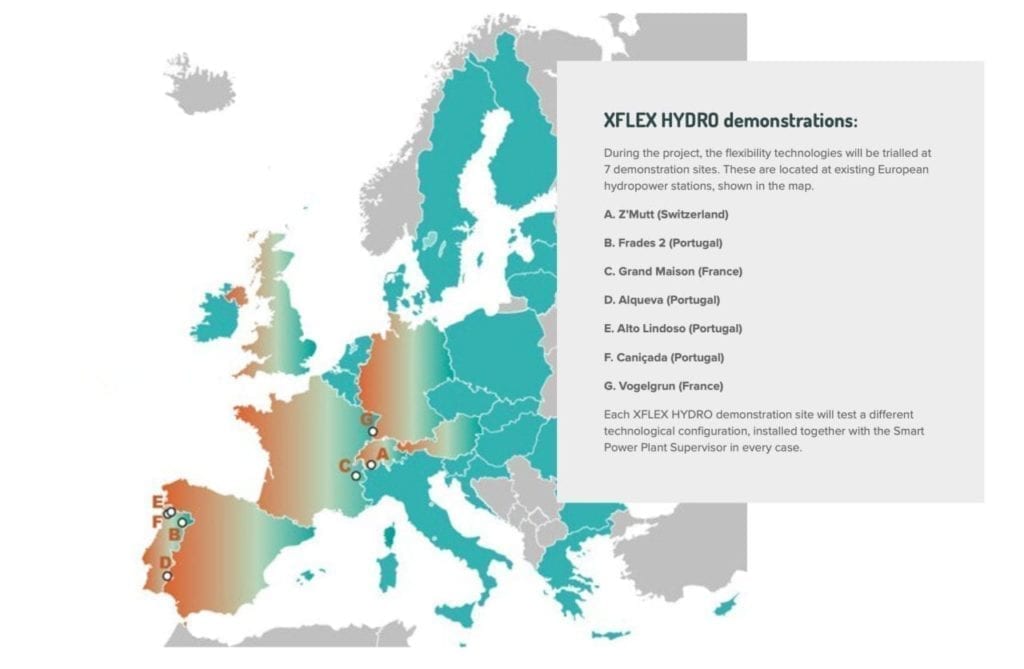
The four-year XFLEX HYDRO (Hydropower Extending Power System Flexibility) project announced at the ongoing United Nations (UN) climate change conference (COP25) in Madrid, Spain, will demonstrate flexibility technologies at seven projects across Europe. Courtesy: XFLEX HYDRO
Z’Mutt (Switzerland). Spearheaded by Switzerland’s largest energy service provider, Alpiq, this project will demonstrate the high flexibility of a 5-MW variable speed hydro unit when equipped with a full-size frequency converter (FSFC) for advanced control capabilities. Enhanced services will include fast-power injection or absorption in pumping and generating mode, inertia emulation, fast-start and stop sequences, as well as fast transitions in turbine and pumping modes.
Frades 2 (Portugal). At this project, EDP Produção and global technology company Voith—which on Dec. 10 announced it would only purchase carbon-neutral power from 2022 onwards—will extend the power range of the existing 390-MW pumped storage (a 2018 POWER magazine Top Plant) through integration of hydraulic short circuit technology for variable speed machines, and increase the potential of renewable dispatchable technologies. The demonstration will also seek to enhance high-quality flexibility services of the electric power system by implementing inertia emulation and frequency containment reserve, and increase annual energy production by reducing auxiliary equipment power consumption.
Grand Maison (France). EDF and GE Renewable Energy (GE) will pair to demonstrate the simultaneous use of very high head pumps and Pelton turbines at this 154-MW pumped storage plant. They will also work to demonstrate the “corresponding enhancement of flexibility services for the power system, thanks to an innovative system integration of hydraulic short circuit technology.”
Alqueva (Portugal). EDP Centre for New Energy Technologies (EDP CNET) and GE will meanwhile evaluate low capital expenditure (CAPEX) opportunities to extend services offered by this existing 130-MW fixed-speed pumped storage plant and compare them to a conversion to variable speed. Efforts will include extending the operating range to target an almost continuous power output from near-zero to rated power in generating mode. They will also test simultaneous pumping and generating through hydraulic short circuit operation.
Alto Lindoso (Portugal). EDP and GE will also pursue a demonstration that is similar to the Alqueva project in overall objectives—which is to look at CAPEX-lowering opportunities—but apply them to the existing 317-MW high-head, large-output reservoir storage hydropower plant at this site.
Caniçada (Portugal). At this 1955-built medium-head 35-MW reservoir storage plant, EDP and GE will pair again to assess the potential of enhanced system integration of the full-scale frequency converter technology at this type of hydropower site. But owing to high costs for a potential conversion, the demonstration will be carried out only through numerical simulations and a software-in-the-loop reduced scale model on an electrical test bench.
Vogelgrun (France). Finally, EDF and Andritz will hybridize this plant’s 35-MW run-of-the-river turbine unit with a battery “of suitable energy capacity and power converter rating” to improve its ability to provide primary frequency response. The partners will also try to significantly reduce turbine wear and tear and quantify it, and evaluate the possibility of upgrading the fixed speed double-regulated Kaplan turbine units with an enhanced variable speed single-regulated propeller unit.
Flexibility Crucial for Hydropower Future
According to the International Hydropower Association (IHA), which will spearhead XFLEX HYDRO project communications, the project will conclude in 2023 with the delivery of a roadmap that could enable increased adoption of the technologies across the hydropower fleet. The roadmap will include policy and market recommendations for governments, regulators, and industry.
As the international nonprofit membership group that is committed to advancing hydropower noted in its May 2019–released Hydropower Status Report, in 2018, global power generation from hydropower reached a record 4,200 TWh, producing almost two-thirds of the world’s renewable electricity generation. However, the IHA also noted a growing number of assets are due for modernization, and it predicts that by 2030, more than half of the world’s existing hydropower facilities will have undergone, or will be due to undergo, upgrading and modernization. By 2050, it predicts all current hydropower facilities will require modernization.
“To ensure that existing assets are retained and available to meet the future role of hydropower in energy systems, traditional modernisation practices will need to consider more than just ‘business as usual’ replacements,” it says. “Major refurbishment projects will look at both improved performance and innovative technologies. For example, fast response capability and optimised operating modes can ensure that hydropower assets have the flexibility to support higher penetrations of variable renewables.”
Along with promoting the XFLEX HYDRO project, the group says that it also working to gain insights on how organizations are improving equipment design to provide four key tenets that could ensure the sector’s future role in changing energy markets: greater functionality and flexibility; enhanced grid support; reduced operating costs; and resilience to climate change.
“We need to decarbonise the power sector, and fast, if we are to limit the devastating impacts of climate change. Last month’s UN Emissions Gap Report is a stark reminder that we need hydropower to boost the contribution of variable renewables like wind and solar,” said IHA Chief Executive Eddie Rich in a statement on Tuesday.
“The XFLEX HYDRO initiative represents a clear commitment by the European Commission, leading organisations from the hydropower sector and academia to invest in new and innovative hydropower technologies,” he added.
—Sonal Patel is a POWER senior associate editor (@sonalcpatel, @POWERmagazine)
The post Hydropower Industry Launches Major International Project to Demonstrate Flexibility appeared first on POWER Magazine.